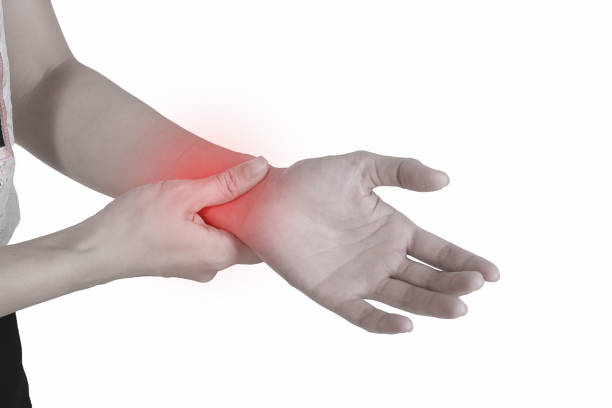
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects the hand and arm, causing numbness, tingling, and weakness. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. While various factors contribute to the development and exacerbation of CTS, diet plays a crucial role in managing symptoms and promoting overall well-being.
1. Introduction to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
What is CTS?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition characterized by pressure on the median nerve in the wrist, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and arm.
Symptoms of CTS
Common symptoms include pain or numbness in the thumb, index, and middle fingers, as well as weakness in the hand and difficulty gripping objects.
2. Importance of Diet in Managing CTS
Dietary choices can significantly impact inflammation levels and nerve health, making proper nutrition essential for individuals with CTS.
Impact of Diet on Inflammation
Certain foods can increase inflammation in the body, exacerbating symptoms of CTS and hindering recovery.
Connection Between Diet and Nerve Health
Nutrient-rich foods support nerve function and can help alleviate discomfort associated with CTS.
3. Foods That Aggravate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Certain foods can exacerbate inflammation and worsen symptoms of CTS, making them important to avoid or limit in the diet.
High-Sodium Foods
Excessive sodium intake can lead to fluid retention and increased swelling, worsening symptoms of CTS.
Processed Foods
Processed foods often contain unhealthy fats and additives that contribute to inflammation and may exacerbate CTS symptoms.
Sugary Snacks and Beverages
High-sugar foods and beverages can spike blood sugar levels, leading to inflammation and potentially aggravating CTS symptoms.
4. The Role of Inflammatory Foods
Certain foods high in trans fats and saturated fats can promote inflammation in the body, exacerbating symptoms of CTS.
Foods High in Trans Fats
Trans fats, commonly found in fried and processed foods, can increase inflammation and contribute to nerve compression in individuals with CTS.
Red Meat and Dairy Products
Red meat and dairy products high in saturated fats may exacerbate inflammation and worsen symptoms of CTS when consumed in excess.
5. Foods High in Refined Carbohydrates
Refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and pastries, can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels and increased inflammation in individuals with CTS.
Effect of Refined Carbs on Inflammation
Refined carbohydrates lack fiber and essential nutrients, leading to rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels, which can exacerbate CTS symptoms.
Alternatives to Refined Carbohydrates
Choosing whole grains and complex carbohydrates can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation associated with CTS.
6. Foods with High Levels of Added Sugars
Excessive consumption of foods high in added sugars can contribute to inflammation and may worsen symptoms of CTS.
Impact of Excess Sugar on Inflammation
Added sugars can promote inflammation in the body, exacerbating symptoms of CTS and hindering recovery.
Healthy Alternatives to Satisfy Sweet Cravings
Opting for naturally sweet foods such as fruits or incorporating small amounts of natural sweeteners can help satisfy cravings without worsening CTS symptoms.
7. The Importance of Maintaining Proper Hydration
Proper hydration is essential for overall health and can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of CTS.
Connection Between Dehydration and Inflammation
Dehydration can lead to increased inflammation and may worsen symptoms of CTS, highlighting the importance of adequate fluid intake.
Best Hydrating Options for CTS Patients
Choosing water and hydrating foods such as fruits and vegetables can help maintain proper hydration levels and support overall well-being in individuals with CTS.
8. Incorporating Anti-Inflammatory Foods into the Diet
Including foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and promote nerve health in individuals with CTS.
Fruits and Vegetables Rich in Antioxidants
Colorful fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants, which can help combat inflammation and support overall health in individuals with CTS.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Their Benefits
Fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and may help alleviate symptoms of CTS.
9. Portion Control and Balanced Eating
Maintaining portion control and consuming a balanced diet are crucial for managing CTS symptoms and promoting overall health.
Importance of Moderation
Eating balanced meals in appropriate portions can help prevent spikes in blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation in individuals with CTS.
Balanced Meals for Overall Health
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can support overall well-being and help manage symptoms of CTS.
10. The Significance of Nutrient-Dense Foods
Choosing nutrient-dense foods provides essential vitamins and minerals necessary for nerve function and overall health.
Whole Grains and Their Benefits
Whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, and oats are rich in fiber and nutrients, supporting optimal nerve function and reducing inflammation in individuals with CTS.
Lean Proteins for Muscle Health
Lean proteins such as poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes provide essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair and function, which is particularly important for individuals with CTS.
11. Lifestyle Changes to Complement Diet
In addition to dietary modifications, adopting certain lifestyle changes can further support the management of CTS symptoms.
Importance of Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity can help improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and alleviate symptoms of CTS.
Ergonomic Adjustments in the Workplace
Making ergonomic adjustments to workspace setups can help reduce strain on the wrists and hands, decreasing the likelihood of exacerbating CTS symptoms.
12. Seeking Professional Guidance
Individuals with CTS should consult healthcare providers or nutritionists for personalized dietary recommendations and guidance.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider or Nutritionist
A healthcare provider or nutritionist can provide tailored advice and recommendations based on individual needs and medical history.
Individualized Dietary Recommendations
Customized dietary recommendations can help individuals with CTS make informed choices to manage symptoms and promote overall well-being.
13. Precautions to Take While Making Dietary Changes
When making dietary changes to manage CTS symptoms, it’s essential to proceed gradually and monitor symptoms closely.
Gradual Modifications for Sustainable Results
Gradually incorporating dietary changes allows for sustainable habits and helps identify any foods that may exacerbate CTS symptoms.
Monitoring Symptoms and Adjusting Diet Accordingly
Regularly monitoring symptoms and adjusting the diet as needed can help individuals with CTS identify triggers and manage symptoms effectively.
14. Success Stories and Testimonials
Real-life success stories and testimonials can provide inspiration and motivation for individuals managing CTS through diet and lifestyle changes.
Real-Life Experiences of Individuals Managing CTS
Stories of individuals who have successfully managed CTS symptoms through dietary modifications and lifestyle changes can offer hope and encouragement to others facing similar challenges.
Inspiration for Those Seeking Dietary Changes
By sharing experiences and insights, individuals with CTS can inspire others to make positive changes to their diet and lifestyle to improve their quality of life.
15. Conclusion
In conclusion, adopting a CTS-friendly diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods and nutrient-dense options can help alleviate symptoms and promote overall well-being. By avoiding foods that exacerbate inflammation and incorporating healthy alternatives, individuals with CTS can take proactive steps to manage their condition and improve their quality of life.